Unlocking Value: The Market Value Approach to Business Valuation
What Is The Market Approach?
The market approach is a commonly used method for determining the value of an asset by analyzing the selling prices of comparable assets. This approach is one of three widely recognized valuation methods, alongside the cost approach and discounted cash-flow analysis (dcf).
Irrespective of the nature of the asset in question, the market approach involves analyzing recent sales data of similar assets and adjusting account for any differences between them. For instance, when evaluating real estate, adjustments may be made based on factors such as the size of the property, the age and location of the building, and its amenities.
Market Value Approach Business Valuation
The market value approach in business valuation involves assigning a value to a business based on market forces in comparable situations. These situations may include a prior transaction involving the same business, an ownership transfer transaction with a comparable (public or private) company, or a market quote of listed securities of a comparable public company.
How Does The Market Approach Work?
The primary advantage of the market value approach lies in its reliance on publicly available data from comparable transactions, reducing the need for a high number of assumptions compared to other valuation methods. Utilizing the market value approach for business valuation is particularly appropriate in the following scenarios:
- When there is a need to substantiate the value of the business in cases of disputes, such as buyouts or disagreements among partners.
- When there is a requirement to support the valuation of the business in discussions with tax authorities or in legal disputes.
- When determining the offer price or asking price for a business acquisition.
Example Of Utilizing The Market Approach
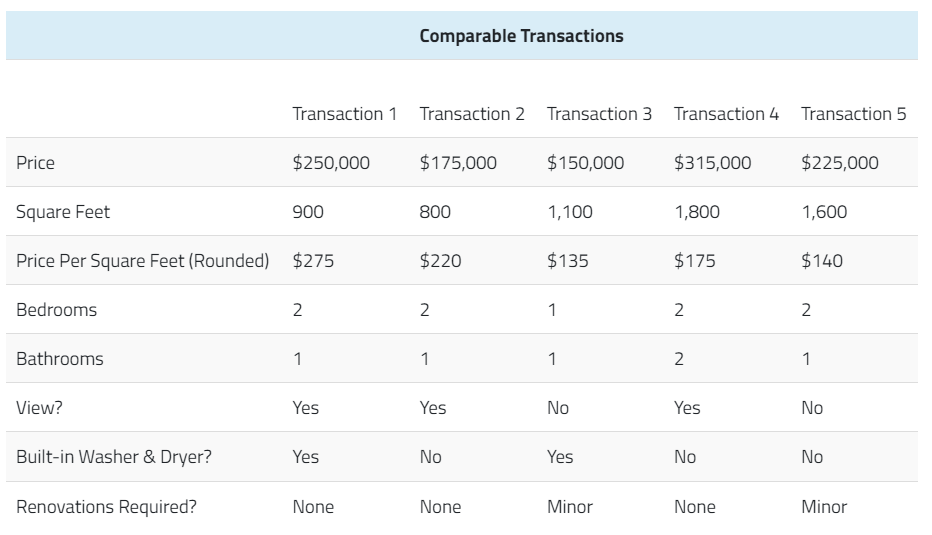
Let's consider a real estate scenario to better illustrate this methodology. Assuming you are in the market for a new apartment, you come across a listing for a 1,000 square-foot apartment with one bedroom and one bathroom in your desired neighborhood, priced at $200,000. While the apartment is in good condition, it requires some minor renovations and lacks certain amenities such as a built-in washing or drying machine. Despite its location, you believe the asking price is too high, especially given its limited view.
After the listing has been on the market for over a month, you decide to negotiate with the seller. To determine a fair market value for the property, you research similar apartments in the area. By analyzing comparable transactions, you find that apartments in the neighborhood have sold for prices ranging from $135 to $275 per square foot. Properties at the higher end of this range typically offer more amenities and features, while those at the lower end may require renovations.
In comparison, the apartment you are interested in is priced at $200 per square foot and lacks some of the desirable features seen in higher-priced units. Based on this information, you believe a lower offer is justified. After careful consideration, you make an offer of $150,000, which is accepted by the seller.
Market Value Approach Methods
Having established an understanding of the market value approach in business valuation, let us now explore the various types that exist. There are numerous classifications within this approach, depending on the origin of the known values utilized as reference points. However, our focus will be on discussing the two primary types that are most commonly employed. These include:
- Public company comparables method : One common valuation method utilized is the public company comparables method. This approach involves analyzing the valuation metrics of publicly traded companies that closely resemble the subject entity. Achieving direct comparability can be challenging, as many public companies tend to be large and have different characteristics than the subject company. It is important to be somewhat flexible in establishing the direct comparability threshold to ensure that public companies with similar business features are not overlooked when valuing the subject company. While direct comparability is feasible in certain industries, many face challenges due to differences between private and public entities. Selecting, adjusting, and applying public company valuation data is a complex process that requires significant experience and expertise. The guideline companies chosen should be publicly traded companies in a similar industry as the subject company, with similarities in financial structure, operational processes, and market dynamics to provide a meaningful basis for comparison in the valuation process.
- Precedent Transactions Method : The second method utilized is the precedent transaction method, which involves determining value through pricing multiples based on observed transactions within the same industry as the subject company. This method assumes that comprehensive financial data for the company is not readily available, but transaction values are accessible. Precedent transactions can be analyzed using industry classification methods, such as SIC codes. Various valuation databases can also be examined for historical actuals and valuation evidence. These transactions may vary in scale and scope, with an ideal transaction being one from a comparable company in the same industry. If direct comparability is not possible, alternative data sources can be utilized after considering factors such as products and market. The precedent transaction method can be useful in situations involving a potential purchase or sale, or as part of a company's exit strategy. However, a key limitation is that some transactions may have occurred in different market or industry conditions, which may not accurately reflect the current acquisition and merger environment. Another challenge is the lack of public information or research data available for determining the suitability of a transaction as comparable data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the market value approach is a key method for business valuation. It can provide valuable insights into the worth of a company, particularly when comparable firms are available for comparison. It is important to note that for small sole proprietorships, alternative valuation methods such as the income-based approach may be more suitable.